When we imagine ancient civilizations, we often think of rudimentary tools or simple lifestyles. Some even had bizarre rituals. But what if I told you that some ancient societies were more sophisticated than you'd expect? These remarkable cultures invented technologies, built awe-inspiring architecture, and developed systems of governance and science that still impress us today. They accomplished incredible feats with limited tools, proving that ingenuity knows no bounds. Join us as we explore the advanced achievements of several ancient civilizations, including their groundbreaking contributions to fields like engineering, astronomy, medicine, and urban planning. From intricate drainage systems to timeless philosophies, these examples of human progress remind us just how inventive our ancestors were.
1. Mesopotamia – The Pioneers of Civilization
Often referred to as the "cradle of civilization," Mesopotamia deserves its reputation. This region, located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, was home to many "firsts" in human history. Their most groundbreaking invention was writing. The Mesopotamians developed a script called cuneiform around 3200 BCE to keep records, which later expanded to include laws, stories, and administrative texts.
Another major contribution was the wheel. Despite what you might think, it wasn’t initially used for transportation. It began as a potter's wheel and was only adapted for carts and chariots around 3000 BCE. Mesopotamians also excelled in farming, creating advanced irrigation systems that used canals to transform dry land into fertile fields. Their achievements in mathematics, such as dividing time into 60-minute hours, are still the foundation of how we measure time today. It’s safe to say that without these early innovators, the course of human history might look very different.
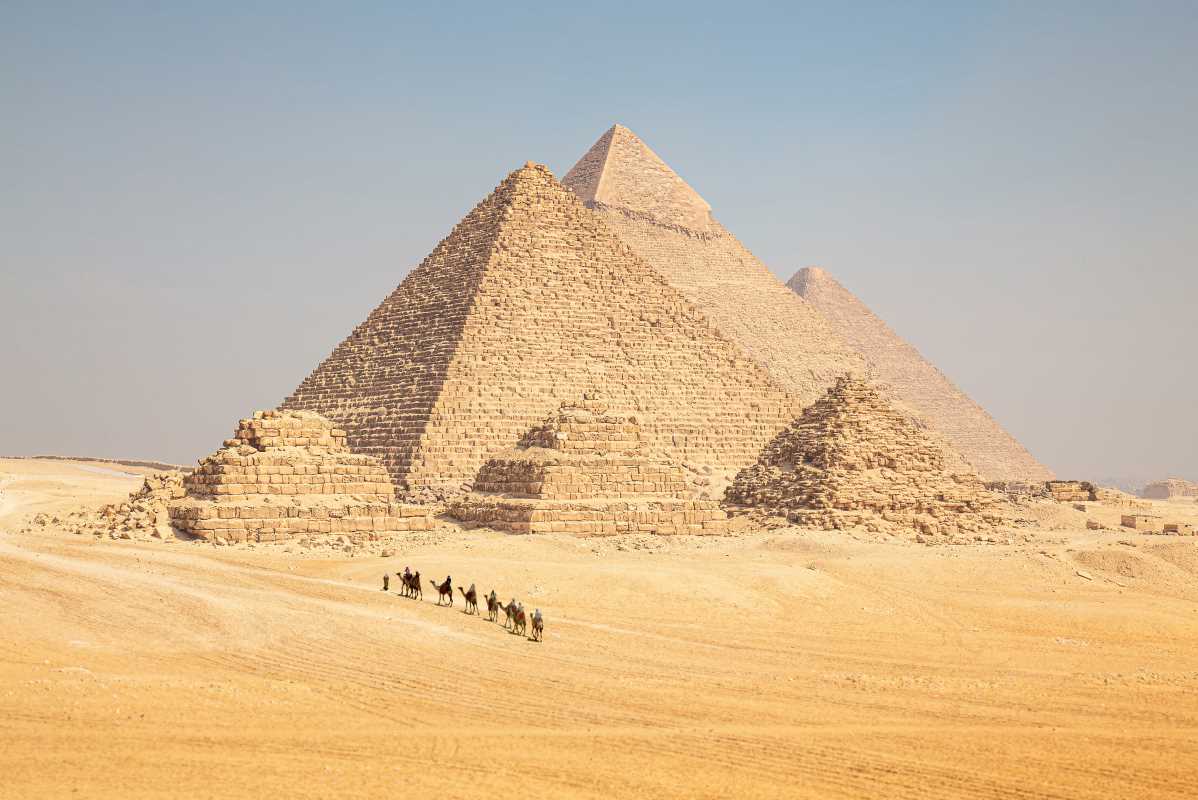
2. Ancient Egypt – Masters of Medicine and Monumental Architecture
Ancient Egypt is best known for its pyramids, but their advancements go far beyond these awe-inspiring structures. The Great Pyramid of Giza, built around 2560 BCE, continues to amaze engineers. The precision required to construct a 480-foot pyramid aligned closely with the cardinal points of a compass without modern machinery is extraordinary. Though historians debate the method, it’s likely they relied on intricate knowledge of geometry and simple tools like ramps and pulleys.
Egyptians were also pioneers in medicine. Using their knowledge gained from mummification, they performed surgeries, treated broken bones, and developed an extensive pharmacopoeia. For instance, remedies detailed in the Ebers Papyrus (c. 1550 BCE) include over 800 medicinal formulas. While their medical practices were intertwined with spiritual beliefs, they understood the value of cleanliness and had surgical tools that resemble some we use today.
3. The Indus Valley Civilization – Urban Planners Extraordinaire
The cities of the Indus Valley Civilization, like Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa, are among the earliest examples of sophisticated urban planning. This civilization, which thrived around 2500 BCE in present-day India and Pakistan, designed its cities with straight streets laid out in a grid pattern. The real marvel was their drainage systems. Many homes had private bathrooms connected to a centralized sewage system, a luxury that wouldn’t become common in Europe until centuries later.
The Indus Valley people were also accomplished craftsmen. Their standardized weights and measures reveal an advanced understanding of trade, while their intricate beadwork and pottery demonstrate artistic skill. Although we’ve yet to decode their written language, the evidence left behind speaks volumes about their innovation and organization.
4. Ancient China – Innovators Who Shaped the World
China’s ancient achievements are nothing short of revolutionary. One of their most influential contributions is paper, invented around 105 CE during the Han Dynasty. Before this, people relied on bamboo or silk for writing, but paper made recording information easier and cheaper, paving the way for books and education.
Gunpowder was another game-changing invention. Developed during the Tang Dynasty around the 9th century, it was initially used for fireworks before becoming critical in military technologies such as cannons and firearms. Even navigation owes much to China, with the magnetic compass enabling explorers to chart new trade routes. And let's not forget the ingenuity required to build landmarks like the Great Wall, which spans thousands of miles and required advanced engineering skills to construct in such harsh conditions.
5. The Maya – Astronomers and Engineers
The Maya civilization, based in Central America, is renowned for its intricate calendar system. Far more than just a tool for marking time, the Mayan calendar was an astronomical wonder. By carefully observing the skies, the Maya could predict solar eclipses and track celestial events with remarkable accuracy, even though they had no telescopes.
The Maya also demonstrated engineering expertise. Their cities, such as Tikal and Copán, were filled with massive stone structures, temples, and reservoirs designed to collect rainwater. The latter was particularly crucial in regions with inconsistent rainfall. They established a system of agriculture, known as milpa, that worked in harmony with their challenging environment, ensuring sustainability.
Culturally, the Maya left a rich legacy of hieroglyphics and art that continues to shed light on their daily life, beliefs, and accomplishments.
6. Ancient Greece – Philosophers and Democracy Builders
Ancient Greece gave the world many gifts, with democracy being one of the most impactful. While modern-day democracies are different, Athens’ system allowed free male citizens to vote and take part in governance. Although it excluded women, slaves, and foreigners, it marked a significant shift toward citizen-led governance.
Greek thinkers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle asked profound questions about ethics, existence, and politics, laying the foundation for Western philosophy. Their architectural marvels, like the Parthenon, showcase their engineering prowess, combining functionality with aesthetic brilliance. Advances in science and mathematics, such as Euclid’s geometry and Archimedes’ principles, continue to influence our world.
7. Ancient Rome – Infrastructure Legends
The Romans were unparalleled when it came to infrastructure. Their aqueducts, for example, brought fresh water to cities, enabling urban centers to grow and thrive. Many Roman roads, constructed with layers of stones and concrete, are still in use today, highlighting the durability of their engineering.
Roman innovation wasn’t limited to physical construction. They developed legal systems, some aspects of which serve as the foundation for modern laws. Public spaces, like the Colosseum, were designed not only for entertainment but also as demonstrations of architectural ingenuity and political power.
The genius of these civilizations lies in their ability to adapt to their environment and solve complex problems with limited tools and knowledge. Despite the time that has passed, their achievements still inspire wonder and respect. These ancient civilizations remind us that innovation and creativity are timeless human traits, capable of transforming any era.
 (Image via
(Image via